SpringBoot获取http请求参数的方法
七种方法
-
直接把表单里面的参数写进 Controller 相应方法的形参中去,这个获取参数的方法适合get提交,而不适合post提交。
url形式:http://localhost/jayvee/demo/addUser?username=wjw&password=123456提交的参数名称必须和Controller方法中定义的参数名称一致。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12/**
* 1.直接把表单的参数写在Controller相应的方法的形参中
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
public String addUser(String username,String password) {
System.out.println("username is:"+username);
System.out.println("password is:"+password);
return "demo/index";
} -
使用 HttpServletRequest 获取参数,适用于post和get方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13/**
* 2、通过HttpServletRequest接收
* @param request
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
public String addUser(HttpServletRequest request) {
String username=request.getParameter("username");
String password=request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username is:"+username);
System.out.println("password is:"+password);
return "demo/index";
} -
通过建立一个bean来获取参数,适用于post和get。
首先创建一个和表单对应的bean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17package demo.model;
public class UserModel {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}使用创建的 bean 来封装接收到前端传来的参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11/**
* 3、通过一个bean来接收
* @param user
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/addUser")
public String addUser(UserModel user) {
System.out.println("username is:"+user.getUsername());
System.out.println("password is:"+user.getPassword());
return "demo/index";
} -
通过 PathVariable 获取传进的参数。
例如,访问http://localhost/jayvee/demo/addUser4/wjw/123465时,则自动将URL中模板变量{username}和{password}绑定到通过@PathVariable注解的同名参数上,即入参后username=wjw、password=123465。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12/**
* 4、通过@PathVariable获取路径中的参数
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/addUser/{username}/{password}",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String addUser(@PathVariable String username,@PathVariable String password) {
System.out.println("username is:"+username);
System.out.println("password is:"+password);
return "demo/index";
} -
使用@ModelAttribute注解获取POST请求的FORM表单数据
jsp表单
1
2
3
4
5
6<form action ="<%=request.getContextPath()%>/demo/addUser5" method="post">
用户名: <input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
密 码: <input type="password" name="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
<input type="reset" value="重置"/>
</form>Java Controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11/**
* 5、使用@ModelAttribute注解获取POST请求的FORM表单数据
* @param user
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/addUser",method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String addUser(@ModelAttribute("user") UserModel user) {
System.out.println("username is:"+user.getUsername());
System.out.println("password is:"+user.getPassword());
return "demo/index";
} -
用注解@RequestParam绑定请求参数到方法入参
当请求参数username不存在时会有异常发生,可以通过设置属性required=false解决,例如: @RequestParam(value=“username”, required=false)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12/**
* 6、用注解@RequestParam绑定请求参数到方法入参
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/addUser",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String addUser(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") String password) {
System.out.println("username is:"+username);
System.out.println("password is:"+password);
return "demo/index";
} -
用注解@RequestBody绑定请求参数到方法入参 用于POST请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14/**
* 7、用注解@Requestbody绑定请求参数到方法入参
* @param username
* @param password
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/addUser",method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String addUser(@RequestBody UserDTO userDTO) {
System.out.println("username is:"+userDTO.getUserName());
System.out.println("password is:"+userDTO.getPassWord());
return "demo/index";
}
//UserDTO 这个类为一个实体类,里面定义的属性与URL传过来的属性名一一对应。
springbooot里的@RequestParam与@RequestBody
-
问题描述
由于项目是前后端分离,因此后台使用的是springboot,做成微服务,只暴露接口。接口设计风格为restful的风格,在get请求下,后台接收参数的注解为RequestBody时会报错;在 post请求下,后台接收参数的注解为RequestParam时也会报错。
-
问题原因
由于spring的RequestParam注解接收的参数是来自于requestHeader中,即请求头,也就是在url中,格式为xxx?username=123&password=456,而RequestBody注解接收的参数则是来自于requestBody中,即请求体中。
-
解决方法
因此综上所述,如果为get请求时,后台接收参数的注解应该为RequestParam,如果为post请求时,则后台接收参数的注解就是为RequestBody。附上两个例子,截图如下:
get请求

post请求

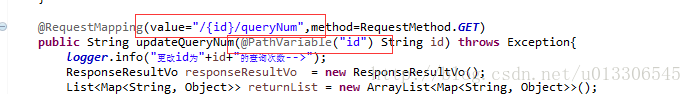
另外,还有一种应用场景,接口规范为resultful风格时,举个例子:如果要获取某个id下此条问题答案的查询次数的话,则后台就需要动态获取参数, 其注解为@PathVariable,并且requestMapping中的value应为value=“/{id}/queryNum”,截图如下: