Spring之DI的使用
什么是DI
Dependence Injection 依赖注入(依赖注射)把一个组件的值设置给另外一个组件的过程叫依赖注入
DI解决的问题就是组件的装配问题
DI的三种实现方式
新建Card.class,并输入
1 | import java.io.Serializable; |
新建Player.class,并输入
1 | public class Player { |
新建applicationContext.xml,并输入
1 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
-
setter注入
参考类型对应的set方法来进行值的设置
在bean标记中出现如下配置
属性名这是设置值,所以参考的是set方法去掉set然后首字母小写
如果要赋值复杂的值则需要使用ref,value能赋值的类型有八种基本类型和封装类、String、枚举
在刚刚新建的applicationContext.xml的beans标签下输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16<!-- 创建一张扑克牌 -->
<bean id="card" class="bean.Card" lazy-init="true">
<property name="suit" value="黑桃"></property>
<property name="point" value="A"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="card2" class="bean.Card" lazy-init="true">
<property name="suit" value="黑桃"></property>
<property name="point" value="K"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 给Player 赋值 高进 65 1 -->
<bean id="player" class="bean.Player">
<property name="name" value="高进"></property>
<property name="age" value="65"></property>
<property name="money" value="1"></property>
<property name="card" ref="card2"></property>
</bean>新建applicationContextTest.class,并输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import bean.Card;
import bean.Player;
public class ApplicationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext app =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Card card = app.getBean("card", Card.class);
System.out.println(card);
Player player = app.getBean("player", Player.class);
System.out.println(player);
}
} -
构造器注入
参考的是构造方法的参数,只要构造方法的参数能匹配上则直接调用对应的带参构造,否则报错.
在bean标记中出现如下配置把上面的property标记换成constructor-arg
注意我们可以使用index替换name,index代表参数的编号,编号0开始
在刚刚新建的applicationContext.xml的beans标签下输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10<!-- 构造器注入 -->
<bean id="card3" class="bean.Card" lazy-init="true">
<constructor-arg name="suit" value="黑桃"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="point" value="Q"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="card4" class="bean.Card" lazy-init="true">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="红桃"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="Q"></constructor-arg>
</bean>在刚刚新建的applicationContextTest.class输入
1
2
3
4Card card3 = app.getBean("card3", Card.class);
System.out.println(card3);
Card card4 = app.getBean("card4", Card.class);
System.out.println(card4); -
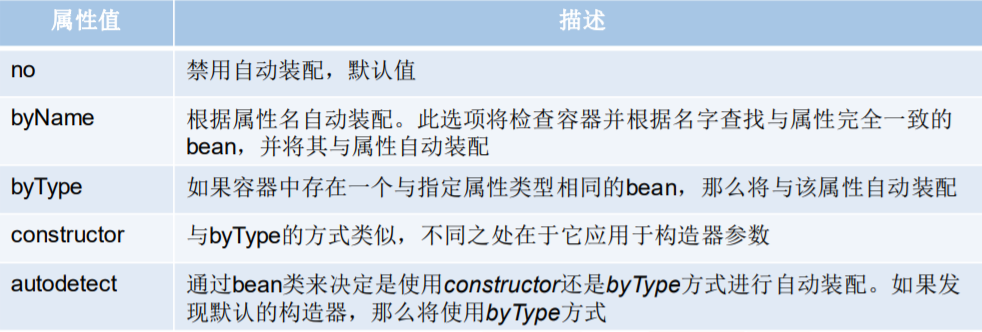
自动化注入
主要解决复杂值的注入问题
只要在bean标记中使用autowire属性指定自动化注入的方式即可
autowire的取值有默认值、byName、byType、constructor
byName参考的是属性名(之前容器定义的id名相同的)、byType参考的是成员变量的类型(之前容器定义的同类型的对象)、constructor参考的是构造方法(构造方法中参数与之前容器定义的类型和名字相同对象)
在刚刚新建的applicationContext.xml的beans标签下输入
1 | <bean id="player2" class="bean.Player" autowire="constructor"> |
在刚刚新建的applicationContextTest.class输入
1 | Player player2 = app.getBean("player2", Player.class); |
参数的注入
新建MsgBean.class,并输入
1 | import java.util.List; |
-
简单值的注入
简单值包括八种基本类型和对应的封装类、String、枚举
练习: 使用连接池的jar包创建dataSource对象,使用容器获取数据源对象(连接池对象)并通过这个对象获取数据库连接
新建applicationContext2.xml,并在beans标签下输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19<!-- 扑克牌的创建 -->
<bean id="card" class="bean.Card">
<property name="suit" >
<value>方片</value>
</property>
<property name="point" >
<null/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 连接池对象的配置 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" >
<value>oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver</value>
</property>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:xe"></property>
<property name="username" value="system"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>新建applicationContextTest2.class,并输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10ApplicationContext app =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext2.xml");
Card card = app.getBean("card", Card.class);
card.setPoint(null);
//System.out.println(card);
if(card.getPoint() == null) {
System.out.println("点数是null");
}
DataSource dataSource = app.getBean("dataSource", DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection()); -
复杂值的注入
把set注入或者构造器注入中的value改成ref,或者自动化注入
-
集合参数的注入
java中有List、Map、Set、Properties,可以在Spring配置文件中配置对应的标记,让其创建出对应的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21List
<list>
<value> 值 </value>
</list>
Set
<set>
<value> 值 </value>
</set>
Map
<map>
<entry key="" value="" />
</map>
Properties
<props>
<prop key="15966667777">小泽</prop>
<prop key="15966667778">伟杰</prop>
<prop key="15966667779">小马</prop>
</props>在刚刚新建的applicationContext2.xml的beans标签下输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88<!-- 创建一个MsgBean 类型的对象 -->
<bean id="msgBean" class="bean.MsgBean">
<property name="title" value="王者农药消息"></property>
<property name="content"
value="晚上约上几个小伙伴 去打一局 从此之后就戒了它"></property>
<property name="friends">
<list>
<value>伟杰</value>
<value>小马弟</value>
<value>杀鱼弟</value>
<value>小泽</value>
<value>小泽</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="friends2">
<set>
<value>伟杰</value>
<value>小马弟</value>
<value>杀鱼弟</value>
<value>小泽</value>
<value>小泽</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="phones">
<map>
<entry key="15966667777" value="小泽"></entry>
<entry key="15966667778" value="伟杰"></entry>
<entry key="15966667779" value="小马"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="phones2">
<props>
<prop key="15966667777">小泽</prop>
<prop key="15966667778">伟杰</prop>
<prop key="15966667779">小马</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 单独定义一个list -->
<util:list id="ref_friends">
<value>伟杰</value>
<value>小马弟</value>
<value>杀鱼弟</value>
<value>小泽</value>
<value>小泽</value>
</util:list>
<util:set id="ref_friends2">
<value>伟杰</value>
<value>小马弟</value>
<value>杀鱼弟</value>
<value>小泽</value>
<value>小泽</value>
</util:set>
<util:map id="ref_phones">
<entry key="15966667777" value="小泽"></entry>
<entry key="15966667778" value="伟杰"></entry>
<entry key="15966667779" value="小马"></entry>
</util:map>
<util:properties id="ref_phones2">
<prop key="15966667777">小泽</prop>
<prop key="15966667778">伟杰</prop>
<prop key="15966667779">小马</prop>
</util:properties>
<!-- Properties 单独定义 但是要关联一个.properties的配置文件 -->
<util:properties id="ref_db" location="db.properties">
</util:properties>
<!-- 创建一个MsgBean 类型的对象 -->
<bean id="msgBean2" class="bean.MsgBean">
<property name="title" value="#{ref_db.username}"></property>
<property name="content"
value="晚上约上几个小伙伴 去打一局 从此之后就戒了它2">
</property>
<property name="friends" ref="ref_friends">
</property>
<property name="friends2" ref="ref_friends2">
</property>
<property name="phones" ref="ref_phones">
</property>
<property name="phones2" ref="ref_db">
</property>
</bean>在刚刚新建的applicationContextTest2.class输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7MsgBean msgBean = app.getBean("msgBean", MsgBean.class);
System.out.println(msgBean +"\n" + msgBean.getFriends2()
+"\n" + msgBean.getPhones()+"\n" + msgBean.getPhones2());
MsgBean msgBean2 = app.getBean("msgBean2", MsgBean.class);
System.out.println(msgBean2 +"\n" + msgBean2.getFriends2()
+"\n" + msgBean2.getPhones()+"\n" + msgBean2.getPhones2());


